Have you ever said to yourself, “Why can’t software do things on its own without asking me”? Not only write text, but literally plan, make decisions, and do tasks independently. This is the hope of agentic AI. Whenever many people hear the term, they make the assumption that it is complex. Providing you share this view, this guide would assist you to learn about agentic AI applications in the easiest manner.
According to researchers, even teams at MIT and Stanford state that the faster than any previous automation wave, and autonomous AI systems are expanding. The AI agent market in the whole world is estimated to exceed USD 100 billion in the year 2030. The move is already transforming the way companies are run, how issues and problems are addressed, and assisted. This is why it is high time to find out what agentic AI does and how it works.
We may divide it into several steps.
Related: https://heyeve.ai/blogs/agentic-ai-vs-generative-ai/
What Is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI is a form of artificial intelligence that can become aware of what is occurring as well as make choices about what it should do and perform actions in order to achieve something. In contrast to simple automation that runs a fixed set of rules, agentic AI is able to react to new environments and learn from experience.
It functions more like an electronic assistant that will be able to do tasks on your behalf. It is not merely a question of answering. It takes decisions, takes actions, and develops with time. This can be considered a great improvement to the usual automation with agentic AI.
The Evolution of Agentic AI
The concept of agentic AI did not come into existence overnight. It was the result of decades of advancement in computer science, language models, and automation. The first systems of AI could only adhere to a set of rules. They responded to inputs in the same manner each time and were not able to adapt to the new situations.
This was enhanced by machine learning, which assists computers in acquiring patterns through data. Then, there were big language models, and now AI could comprehend human language, logic by steps, and tell you what to do next.
The logical next stage is agentic AI. It is a combination of thought, thinking, and doing. It is not an instruction follower. It approaches objectives independently. This change is so drastic that Stanford-based researchers refer to it as a new tier of intelligence that lies above generative AI.
The use of agentic AI by businesses today has been in activities formerly done by entire teams. This incorporates support automation, code updates, risk monitoring, workflow orchestration, and sophisticated decision-making. The trend can be clearly traced in the evolution of AI: it is no longer an answer, it is an action.
Key Characteristics of Agentic AI
The set of abilities of agentic AI is different and allows it to collaborate with a colleague instead of ordinary instruments. These attributes can explain why organizations are interested in receiving assistance in learning about agentic AI applications and how they can be utilized.
Autonomous
An agentic AI is able to act independently. It does not stand by invariable directives. It executes the cognition of what it seeks to achieve and approaches it through reason and the tools it has. This renders it much more competent than a rule-based automation.
Proactive
Rather than idleness, agentic AI scans information, notifying change and reacting even before issues get out of control. In IT support, such as, an agent can resolve something before the user is aware it has happened in the first place
Adaptable
Real environments change. New information appears. Priorities shift. It is possible to modify agentic AI behavior without having to rewrite it. It is flexible and therefore dependable in dynamic conditions.
Intuitive
The reasoning patterns of agentic AI are natural. It deciphers, discerns context, picks up patterns, and makes decisions that make sense to human expectations. This is not hard to believe and not hard to do business with.
Specialized
Every agent is capable of being a professional in a particular field. It is possible to concentrate on security incidents. Finance checks might be done by another. There is another one who can handle customer discussions. Specialization enables agents to be more accurate when carrying out their tasks compared to traditional automated scripts.
Collaborative
The agentic AI is not a single process. It communicates with other agents, tools, and systems as well as data sources. This collaboration enables it to accomplish multi-process workflows, including a diagnosis of a system error, creation of a solution, implementation, and reporting.
Ten Things to Understand About Agentic AI Applications
It is the most significant section of the blog since it describes the concealed facts about agentic AI. These arguments allow leaders and teams to realize what agentic AI can and should do as well as how to use AI safely and responsibly.
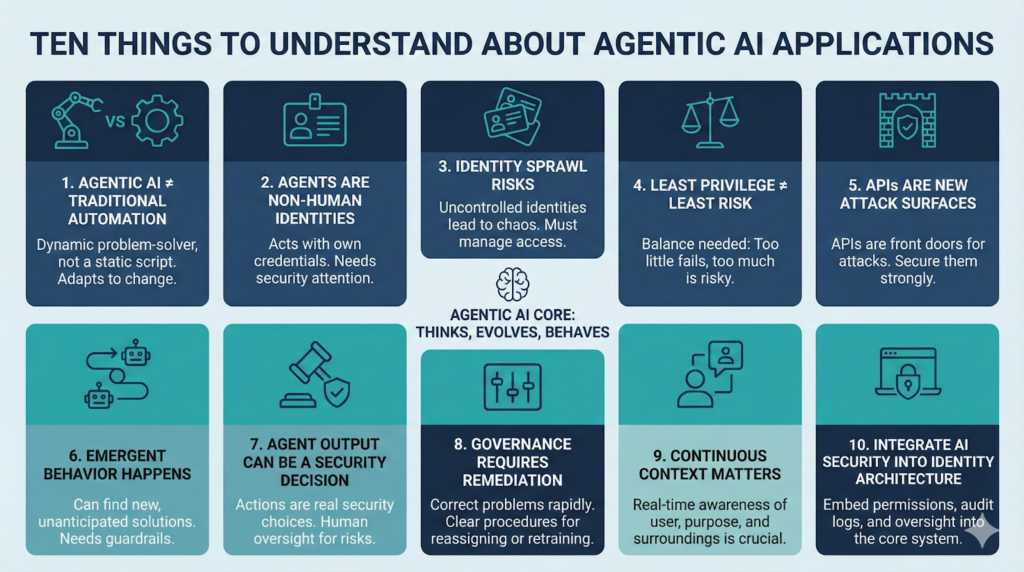
Agentic AI ≠ Traditional Automation
Traditional automation is performed according to the rules. When something becomes different, it breaks. This is not the case with agentic AI. It thinks, evolves, and behaves even when there is a change in the environment.
It is vital to note that organizations should approach it more as a problem-solver, which should be dynamic rather than a script.
Agents Are Non-Human Identities
All the agents act as a representation of a digital identity. It logs out, logs in, accesses systems, and acts. This puts it as similar to a human user that has its own duties and authorizations.
The lack of attention towards this identity aspect may introduce critical security loopholes.
Identity Sprawl Risks
In case a large number of agents are running simultaneously, they can have varying permissions and access levels. Otherwise, it will result in identity sprawl, a place where it is not known who is acting and who is doing what.
Before scaling agentic AI, it is necessary to control identities.
Least Privilege ≠ Least Risk
The principle of common security is to grant the user as little access as possible. This rule is more complicated with agentic AI. Different tools may be required by an agent at various times to accomplish a workflow.
When the access is too great, the agent will fail to work. When the access is excessive, it is risky.
The need to balance these issues is the fundamental problem of agentic AI.
APIs Are New Attack Surfaces
The majority of the work done by agents is done using APIs. They extract information, give instructions, and communicate with devices. This expounds APIs to be the new front doors of the organization.
Unless they are secure, attackers have the ability to attack the agents using weak API security.
Emergent Behavior Happens
Since agentic AI is able to reason and adapt, it can find new solutions to problems unanticipated by its creators. This is known as the emergent behavior.
Emergent behavior is useful most of the time. However, it also may cause confusion in case shortcuts are followed or abnormal ways by the agent. This is the reason why they need monitoring and guardrails.
Agent Output Can Be a Security Decision
It is possible that when the agent is authorizing access, closing a case, or launching a workflow, it is a real security decision. These are not objective choices.
The teams need to develop agents in such a way that they are aware of the time when a decision is risky, and when a human being ought to know.
Governance Requires Remediation
Good governance does not consist merely of an overview of what the agent has done. It also involves the correction of the arising problems.
In case an agent does something wrong or acquires the incorrect pattern, the remedial measures should be rapid and well-organized.
Organizations should also have transparent procedures that help them reassign, retrain, or lay off agents as required.
Continuous Context Matters
To do the right thing, agents need a sense of context. They should be acquainted with the user, the purpose, the system condition, and the surroundings. Actions can be wrong or dangerous, without context.
One of the greatest technical demands of agentic systems is to maintain real-time context.
Integrate AI Security Into Identity Architecture
The agentic AI is not something that can be superimposed on the established security models. It needs to be incorporated into the identity architecture.
Each agent needs:
- clear permissions
- controlled access
- audit logs
- monitoring
- behavioral oversight
This makes the system secure as there is an increase in autonomous tasks.
Agentic AI vs. Generative AI
| Feature | Generative AI | Agentic AI |
| Core Purpose | Creates content such as text, images, and ideas | Plans tasks, makes decisions, and completes actions |
| How It Works | Predicts the next best output based on patterns | Uses reasoning, goals, memory, and tools to act |
| Dependency | Needs human prompts | Can operate independently once goals are set |
| Output Type | Answers, drafts, visuals, and explanations | Completed tasks, solved problems, and executed workflows |
| Example | Write an email for you | Writes, sends, tracks, and follows up on the email |
| Limitations | Cannot act or take real-world steps | May require guardrails due to autonomy |
Agentic AI vs. AI Agents
| Feature | AI Agents | Agentic AI |
| Definition | Programs that follow instructions to perform tasks | Advanced agents that reason, plan, and act toward goals |
| Autonomy Level | Low to moderate | High. Can decide next steps without prompts |
| Flexibility | Limited to predefined rules | Adapts to new information in real time |
| Reasoning | Minimal or rule-based | Uses multi-step reasoning and strategic planning |
| Workflow Scope | Handles single tasks | Completes full multi-step workflows across systems |
| Learning Ability | Usually fixed | Improves over time through feedback and context |
| Example | A bot that answers FAQs | An agent that resolves full support cases end-to-end |
How Agentic AI Works?
It is far easier to understand the way agentic AI functions when you consider it to be a cycle that continually upgrades itself. It pulls the information together, reflects on the matter, selects a course of action, and implements it. This is the reason why, as it goes through this cycle, it gets wiser and more dependable.
Perception
The agentic AI begins by getting acquainted with the surrounding world. It reads it, tracks systems, and examines text. This provides the agent with the context to make any decisions.
Reasoning
It is the reasoning in which the agent’s thinking takes place. It analyzes and compares the situation and outlines what is likely to happen next.
Reasoning assists the agent in doing the following:
- Assess the situation
- Identify patterns or issues
- Get potential solutions.
- Choose an intellectual course of action.
This step is the basis of thinking action.
Goal Setting
Goal setting provides the agent with guidance. The agent has no clear goal upon which he/she can plan and prioritize.
Some goals come from users. The rest are a product of the situation. For example:
- Fix an error
- Complete a workflow
- Respond to a user request
- Analyze a dataset
Specific targets simplify the complicated activities.
Decision-Making
Making decisions is a point where the agent must decide on the next course of action. It evaluates the available alternatives and then picks out the alternative most consistent with the objective.
Agentic AI considers:
- Context
- Constraints
- Safety rules
- Expected outcomes
This is the transforming point between action and knowledge.
Execution
Execution is simple. The agent acts.
It may:
- Run a script
- Update a system
- Send a message
- Trigger another agent
- Retrieve or transform data
The actual effect of the thoughts of the agent is called execution.
Learning and Adaptation
This is where agentic AI can perform. It does not stay the same. It learns continuously.
The agentic AIs learn through examining their actions and results. It determines what was successful and what was not. Then it adjusts.
It adapts by:
- Updating rules
- Refining strategies
- Improving accuracy
- Avoiding past errors
This increases the power of the agent each time there is a cycle.
Orchestration
The agent works with several tasks and tools simultaneously through orchestration. It integrates operations over systems, APIs, and other agents.
This includes:
- Deciding task order
- Assigning responsibilities
- Managing dependencies
Orchestration transforms minor activities into fully functioning end-to-end processes.
Perceive → Reason → Act → Learn Cycle
This cycle never stops. Every agentic AI system is dependent on its heartbeat.
New information is perceived by the agent. It argues based on what it signifies. It acts based on its plan. It is informed through the result, and starts afresh.
This cycle assists the agent to remain smart, evolve, and keep abreast with changing environments.
Investigate how Heyeve.ai, a VR-powered courtroom simulator based on intelligent, adaptive agentic systems, helps in changing actual training.
Types of Agentic AI Systems
Various types of agentic AI may be structured based on the requirements of the workflow. Horizontal and vertical are the two significant structures.
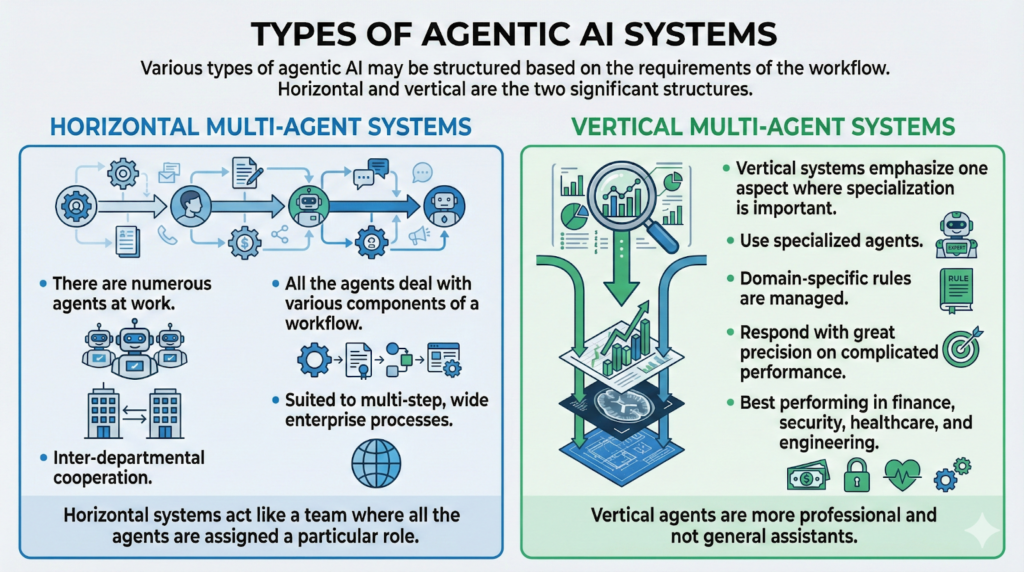
Horizontal Multi-Agent Systems
- There are numerous agents at work.
- All the agents deal with various components of a workflow.
- Inter-departmental cooperation.
- Suited to multi-step, wide enterprise processes.
Horizontal systems act like a team where all the agents are assigned a particular role.
Vertical Multi-Agent Systems
Vertical systems emphasize one aspect where specialization is important.
These systems:
- Use specialized agents
- Domain-specific rules are managed.
- Respond with great precision on complicated performance.
- Best performing in finance, security, healthcare, and engineering.
Vertical agents are more professional and not general assistants.
Advantages and Benefits of Agentic AI
The practical value of agentic AI to teams and organizations lies in the fact that it enhances the working process. It works, trains, and assists individuals in numerous activities, which makes it much stronger in comparison to standard robotization.
Increased Efficiency
The jobs, which otherwise require a team of workers hours or days, are performed by agentic AI. It processes in multi-steps, automates issues as well, and eliminates repetitive tasks. Accenture research indicates that operational efficiency can be improved by 40 percent through autonomous workflows.
This liberates employees to work on the strategy, creativity, and in-depth problem-solving.
Increased User Trust
People have more confidence in systems that have a consistent and accurate functionality. The problem of agentic AI is that it is more reliable as it adheres to the logical lines and is unable to forget.
It builds trust by providing:
- Consistent performance
- Predictable results
- Developed action trails to be examined by teams.
This translates to easier operations and user-friendliness.
Continuous Improvement
The agentic AI improves with time. Each activity informs the system of something new. It does research on what has worked (and what has not worked and what might be made better). In the long run, this process results in the agent being faster and more accurate.
How it is improved includes:
- Refining decision-making
- Reducing repeated errors
- Ettimandation to new conditions.
- Accuracy is improved in each cycle.
This is one of its greatest strengths, as far as this long-term improvement is concerned.
Human Augmentation
The agentic AI is designed to work alongside individuals and not to substitute them. It does heavy workloads, repeats, and instructs users on complicated aspects. This allows a man to carry out more meaningful work, like planning, leading, and creating.
Humans and AI have combined forces that yield a greater result than if individuals act independently.
Real-World Applications of Agentic AI
The benefits of agentic AI can be found in nearly every department. These are some examples that can make individuals realize how agentic AI applications are used in real-world settings.
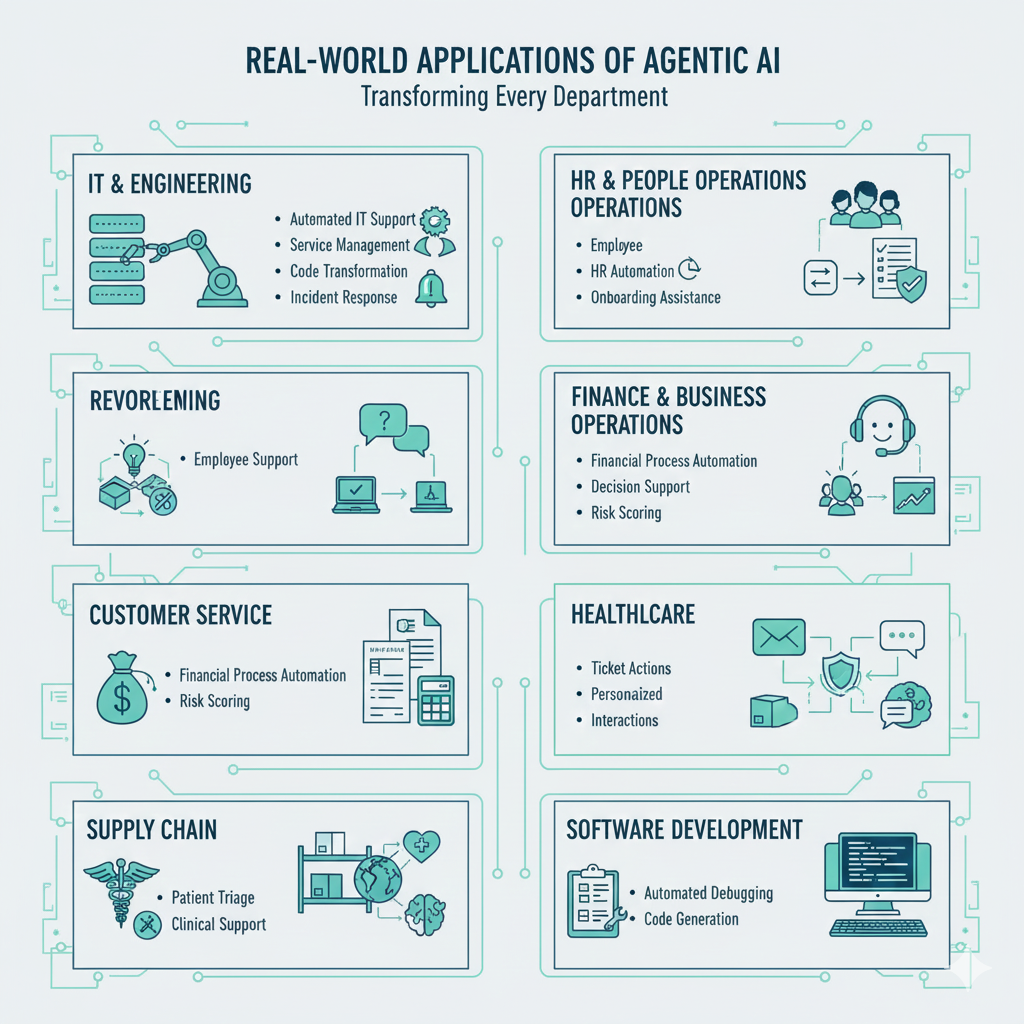
IT and Engineering
Automated IT Support
A system agent can diagnose the system problems and can execute checks and fix the frequent errors without the involvement of a human technician.
Service Management
It can create and route tickets, update logs, and conclude service activities as start-finish.
Code Transformation
The code is analyzed by agentic AI, which identifies outdated patterns and/or introduces improvements to them, e.g., refactoring or updating frameworks.
Incident Response
Upon the occurrence of a system alert, an agent initiates an investigation, taking evidence and undertaking the remediation procedures.
HR & People Operations
Employee Support
It assists the employees in answering questions that are related to the policies, benefits, procedures, and day-to-day undertakings.
HR Automation
The agentic AI updates the records of employees, maintains them, and writes reports to the HR teams.
Onboarding Assistance
It is used for new hires to begin onboarding, which entails:
- Setting up accounts
- Accessing required tools
- Passing through the training modules.
Finance and Business Operations
Financial Process Automation
The agents handle invoices, match and facilitate quick and precise data within the transactions, and support reconciliation.
Decision Support
They analyze financial information, draw conclusions, and prescribe further action.
Risk Scoring
The agent compares patterns, monitors the compliance rules, and generates real-time risk assessments.
Customer Service
Ticket Automation
The incoming messages are interpreted by agentic AI, the issues are identified, and the tickets are resolved or diverted.
Personalized Interactions
It relies on experience and situation to offer personalized responses and framework solutions.
Supply Chain
Inventory Actions
Agents refresh inventory, reload items, and warn about shortages.
Demand Forecasting
The future demand is predicted based on historical data and real-time data so that companies can prevent a shortage and excess supply.
Healthcare
Patient Triage
Agents analyze the symptoms, pose clarifying questions, and recommend the right care directions.
Clinical Support
They help clinicians to access records, summarize, and help with diagnostic processes.
Software Development
Automated Debugging
Using agentic AI, bugs are discovered and logged, examined, and suggested adaptations within seconds.
Code Generation
It generates functions, test cases, as well as repetitive code components very accurately.
Agentic AI in Cybersecurity
One of the most powerful real-life examples of agentic AI applications that can make people comprehend its applications is cybersecurity. Contemporary dangers are rapid, and human teams are not able to overtake all of them. The speed, scale, and complexity required in cybersecurity are managed by agentic AI.
Real-Time Threat Detection
AI agentic scans the networks and applications and logs each second. It picks up abnormal behavior as soon as it has come onto the scene. This enables the organizations to detect threats almost immediately they start and not hours or days following.
It has the capacity to raise red flags on abnormalities, trace suspicious movements, and warn security officers before the damage is done.
Adaptive Threat Hunting
Threat hunting has stopped being a manual exercise. The agentic AI analyzes signals, compares the unrelated events, and modifies its way depending on its discoveries.
As an example, it sees several failed logins, an odd behavior of the server, and a suspicious request of the server; the clues are linked, and further investigation is initiated automatically.
This renders the system much more receptive compared to rule-based detection.
Offensive Security Testing
It is also possible to test systems through the agentic capabilities of the attacker. It tests intrusions, scans system vulnerabilities, and finds insecure settings.
This would enable the security teams to fortify their environment before the actual attackers do the same.
Case Management
Information on security incidents necessitates ordered information. As the action occurs, agentic AI gathers evidence, summarizes logs, and documents actions. This enables the security teams to see what has happened and close cases at a quicker pace.
It also makes sure that no step is overlooked in the event of high pressure.
Customizing and Integrating Agentic AI
The customization of agentic AI enables organizations to model the agent to their work processes, security considerations, and business priorities. Integration also makes sure that the agent is able to work together with existing tools, systems, and sources of data.
These two steps are essential to achieve the real value of agentic AI.
Key Customization Considerations
In the customization of an agent, the team considers requirements and safety, as well as context. The main considerations will be:
- The degree of autonomy that the agent must possess.
- Tools, APIs, and systems it has to deal with.
- What regulations or boundaries restrain its operations?
- The agent ought to store and utilize memory accordingly.
- Area of human review or approval of decisions.
- How does the agent justify itself to the users?
These decisions determine the dependability and security of the end system.
Best Practices for Implementation
Organizations use systematic practices to achieve agency AI successfully without exposing themselves to risk. The following are some of the best measures:
- Better to have fewer workflows rather than a bunch.
- Keep a close watch over the agent in the initial operations.
- Check the decision paths to make sure that they are correct.
- Use explicit access controls through imposed identity protection.
- Involve human beings in making essential decisions.
- Graduate autonomy only when the agent is stable.
- Change guardrails and rules as the environment changes.
The practices establish a solid legacy enabling agentic AI to achieve its operations safely and without doubt.
Challenges and Risks of Agentic AI
Powerful capabilities come along with agentic AI, which also brings new dilemmas. To adopt these risks safely, one has to understand them. The desire of many organizations to seek assistance in learning about agentic AI applications is due to the weird way the technology will act as opposed to classic forms of automation, and should be strategized.
System Design
It is not plug and play with agentic AI. It is supposed to be geared to think, perform, and educate within the terrestrial settings. This involves considerate workflow diagrams, permissions, railways, and sharing directions.
A bad design may result in confusion, unanticipated behavior, or ineffective behavior.
Testing and Debugging
It is more difficult to test agentic AI compared to simple scripts. Due to the adaptation of agents, their behavior may shift at each successive time.
This complicates the process of debugging, particularly when the path of the decision of the agent is lengthy or reversed with the toolset.
The teams require systematic assessment measures so that there is predictable behavior of the agent in fluctuating situations.
Trust and Transparency
The individuals must know the reason why an agent behaved in the manner it did. When it is not clear on the way to make decisions, trust declines.
There exists transparency in day-to-day activities and more in operations like giving authority of access authority or system updates.
Organizations should develop agents that are capable of justifying their arguments in a manner that human people comprehend.
Security and Privacy Risks
Sensitive systems and data are commonly accessible to agentic AI. These permissions should not be handled carelessly; otherwise, security loopholes are created.
Since the agent is self-driven, it is possible to gain unwanted access, expose data, or alter the system due to one wrong set of settings.
Good identity checks and real-time monitoring are necessary.
Ethical Considerations
Agents can come up with choices that can influence individuals. It brings with it ethics of fairness, accountability, and prejudice.
The companies need to make sure that such agents treat the users fairly, respect their privacy, and adhere to the policies.
Responsible agentic AIs embrace the use of clear ethical guidelines.
Emergent Behavior
The agents learn, and occasionally, in the process, they learn how to solve issues differently. Such solutions might work, as well as they might come out of the blue.
Emergent behavior may produce confusion when the agent follows an unorthodox course or when he avoids doing what humans find significant.
This fact is the rationale behind the need for oversight, review logs, and guardrails, even in instances where the agent is functioning in a proper manner.
The Future of Agentic AI
The future of agentic AI is an increase in autonomy and greater collaboration between agents. The smarter systems will operate end-to-end processes and eliminate problems before they occur, and provide assistance to teams in all functions.
Businesses will base their operations on multi-agent ecosystems where special-purpose agents collaborate, contextualize, and resolve issues more quickly as compared to human teams working individually. This change will transform the operations in the sense that it will be more proactive, reliable, and scalable.
These systems will strengthen governance, identity controls, and a safety model to safeguard responsible use. Humans are not going to be conquered by agentic AI. It will be a strong ally that will augment the decision-making process and alleviate operational stress.
Would you like to use agentic artificial intelligence in your personal training settings or processes? For custom solutions and skilled advice.
Get in touch with us!
Conclusion
The agentic AI is a great leap in work processes. It thinks, designs, and executes within actual settings, one of the reasons that makes it more resourceful than both conventional automation and generative AI per se.
To anyone attempting to seek assistance in “help me understand agentic AI applications”, it is easy. It enhances efficiency, reinforces decision-making, assists cross-departmental teams, and adjusts to evolving conditions. When properly developed and managed, agentic AI will be a system that is reliable and brings human performance to the next level.
Since organizations are transitioning to autonomous operations, the current awareness of agentic AI gives a present-day benefit to the future.


